How Do Certain Foods Combat Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects many men worldwide, often leading to significant stress and impacting quality of life. While various medical treatments are available, lifestyle changes, particularly dietary adjustments, can play a crucial role in managing and potentially improving ED. Understanding how certain foods can combat erectile dysfunction can empower individuals to make healthier choices that benefit their sexual health.
The Role of Nitric Oxide in Erectile Function
Nitric oxide (NO) is a vital molecule in the body that plays a significant role in vasodilation, the process where blood vessels widen to increase blood flow. This process is crucial for achieving and maintaining an erection. Foods rich in nitrates and antioxidants help boost NO production. Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are high in nitrates. When consumed, these nitrates are converted into NO, promoting better blood flow to the penis. Additionally, beets are another excellent source of nitrates, and their regular consumption can significantly enhance NO levels in the body.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Oxidative stress is a condition where there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, leading to cell damage. This stress can adversely affect blood flow and contribute to ED. Consuming antioxidant-rich foods can help mitigate this issue. Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are packed with antioxidants, including vitamin C and flavonoids. These compounds help neutralize free radicals, improving blood flow and reducing the risk of ED. Dark chocolate is another potent source of flavonoids and has been shown to improve circulation, benefiting erectile function.
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce on its own, necessitating their intake through diet. These fats have been shown to improve cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation and enhancing blood flow. Given that ED is often linked to poor cardiovascular health, consuming omega-3-rich foods can be beneficial. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s. Additionally, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts provide plant-based omega-3s, making them great alternatives for those who prefer not to eat fish.
Amino Acids and Erectile Function
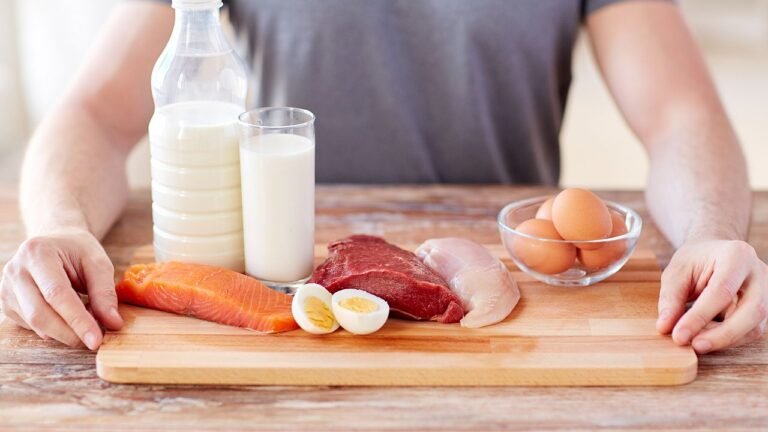
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and play various roles in bodily functions, including the production of NO. L-arginine, an amino acid found in foods such as turkey, chicken, peanuts, and soybeans, is directly involved in NO production. Increased intake of L-arginine can help enhance blood flow to the penis, improving erectile function. Similarly, L-citrulline, another amino acid found in watermelon, can be converted into L-arginine in the body, boosting NO levels and aiding in combating ED.
Zinc and Erectile Health
Zinc is a trace mineral that is crucial for many biological functions, including the production of testosterone, a hormone essential for sexual health. Low levels of testosterone can lead to ED. Consuming zinc-rich foods can help maintain adequate testosterone levels. Oysters are one of the best natural sources of zinc, but other foods like beef, pumpkin seeds, and lentils also provide significant amounts of this mineral. Ensuring a diet with sufficient zinc intake can help improve erectile function and overall sexual health.
The Benefits of a Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, known for its heart-healthy benefits, has also been linked to improved erectile function. This diet emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Olive oil, a staple of the Mediterranean diet, is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, which support cardiovascular health and enhance blood flow. Studies have shown that men who adhere to a Mediterranean diet have a lower incidence of ED. The diet’s emphasis on fresh, unprocessed foods helps reduce inflammation and supports vascular health, both of which are crucial for maintaining erectile function.
Lifestyle and Dietary Patterns
Beyond specific foods, overall dietary patterns and lifestyle choices significantly impact erectile health. A balanced diet that avoids excessive consumption of processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can promote better overall health and reduce the risk of ED. Regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are also important factors. These lifestyle choices help improve cardiovascular health, which is closely linked to erectile function. A holistic approach that combines a healthy diet with positive lifestyle changes can lead to significant improvements in managing and preventing ED.
Foods to Avoid for Better Erectile Health
Just as certain foods can enhance erectile function, others can have detrimental effects. Diets high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed foods can lead to poor cardiovascular health and increase the risk of ED. Excessive alcohol consumption can also impair erectile function. High-fat diets, particularly those rich in saturated and trans fats, can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, restricting blood flow to the penis. Reducing the intake of these harmful foods and beverages can help maintain better erectile health and overall well-being.
The Psychological Impact of Diet on ED
While physical health is a significant factor in ED, psychological factors also play a crucial role. Diet can influence mood and mental health, indirectly impacting erectile function. Foods that support brain health, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins, can improve mood and reduce stress and anxiety, which are common psychological contributors to ED. A balanced diet that supports mental well-being can, therefore, have a positive effect on erectile health.
Conclusion
The relationship between diet and erectile dysfunction is multifaceted, involving the improvement of cardiovascular health, hormone regulation, and mental well-being. Consuming a diet rich in nitrates, antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, amino acids, and zinc can enhance blood flow, support healthy testosterone levels, and reduce oxidative stress, all of which contribute to better erectile function. Adopting dietary patterns such as the Mediterranean diet, combined with healthy lifestyle choices, can provide a holistic approach to managing and potentially reversing ED. By understanding and implementing these dietary changes, individuals can take proactive steps towards improving their sexual health and overall quality of life.